Environmental impact of coal and pellets
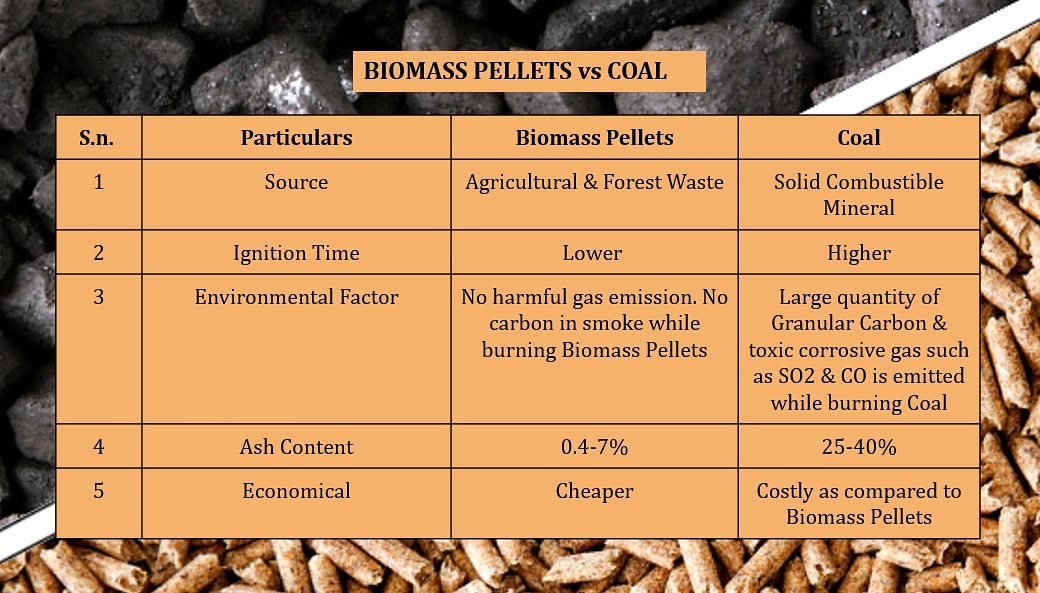
When it comes to choosing a fuel source for heating or power generation, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact. In this article, I will compare the environmental impact of coal vs pellet, two commonly used fuel sources.
By understanding the differences between these two options, we can make informed decisions that contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Coal: a major contributor to air pollution
Coal has long been a popular choice for heating and power generation due to its high heat output. However, it comes with a significant environmental cost. The combustion of coal releases large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Additionally, coal combustion emits sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, all of which contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health.
Pellets: a cleaner and more sustainable option
On the other hand, pellets offer a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to coal. Pellets are made from compressed biomass materials such as wood waste, agricultural residues, or energy crops.
Unlike coal, the combustion of pellets releases significantly lower levels of CO2 and other harmful emissions. Furthermore, the production of pellets utilizes renewable resources, making them a more sustainable choice.
Efficiency and cost comparison

Efficiency and cost are important factors to consider when choosing a fuel source. Let’s compare the efficiency and cost of coal and pellets to understand their differences.
Coal: high heat output but low efficiency
Coal is known for its high heat output, which makes it an attractive option for heating purposes. However, coal has a relatively low efficiency compared to other fuel sources.
This means that a significant portion of the energy contained in coal is wasted during combustion. As a result, more coal is required to produce the same amount of heat compared to more efficient alternatives.
Pellets: efficient and cost-effective
Pellets, on the other hand, offer higher efficiency compared to coal. Due to their uniform size and composition, pellets burn more efficiently, maximizing the heat output.
This increased efficiency translates to cost savings, as less fuel is needed to achieve the same level of heat. Additionally, the availability of pellets in the market has increased in recent years, leading to competitive pricing and making them a cost-effective option.
Availability and accessibility

Availability and accessibility are crucial considerations when choosing a fuel source. Let’s compare the availability and accessibility of coal and pellets.
Coal: limited availability and transportation challenges
Coal reserves are limited and unevenly distributed across the globe. This limited availability can lead to price fluctuations and supply chain challenges. Furthermore, the transportation of coal can be logistically complex and expensive, especially for areas located far from coal mines or ports. These challenges can impact the accessibility and affordability of coal as a fuel source.
Pellets: widely available and easy to transport
Pellets, on the other hand, are widely available and easy to transport. The production of pellets can be decentralized, utilizing locally available biomass materials. This decentralization reduces the reliance on specific regions for fuel supply, making pellets more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Additionally, the compact size and uniform shape of pellets make them easy to transport, reducing logistical challenges and costs.
Health and safety considerations
Health and safety should be paramount when choosing a fuel source. Let’s compare the health and safety considerations of coal and pellets.
Coal: harmful emissions and health risks
Coal combustion releases harmful emissions such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health.
Prolonged exposure to coal combustion byproducts can lead to respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and even cancer. Additionally, the mining and handling of coal pose safety risks for workers, including accidents and exposure to harmful substances.
Pellets: cleaner combustion and reduced health hazards
Pellets offer cleaner combustion compared to coal, resulting in reduced emissions of harmful pollutants. The lower levels of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter make pellets a healthier option for both the environment and human health.
Furthermore, the production of pellets from biomass materials does not involve the same safety risks as coal mining, making them a safer choice for workers.
Renewable energy and sustainability

Renewable energy and sustainability are crucial considerations in the fight against climate change. Let’s compare the renewable energy and sustainability aspects of coal and pellets.
Coal: non-renewable and contributes to climate change
Coal is a non-renewable resource, meaning it cannot be replenished once depleted. The extraction and combustion of coal contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, including CO2, which is a major driver of climate change.
The reliance on coal as a fuel source exacerbates the environmental challenges we face and hinders progress towards a sustainable future.
Pellets: renewable and environmentally friendly
Pellets, on the other hand, are made from renewable biomass materials. These materials can be sustainably sourced and replenished, ensuring a continuous supply of fuel. Additionally, the combustion of pellets releases CO2, but the carbon emitted is part of the natural carbon cycle.
This means that the carbon released during pellet combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed by the biomass during its growth, making pellets a carbon-neutral fuel source.
Conclusion on coal vs pellet
In conclusion, when comparing coal and pellets, it is evident that pellets offer numerous advantages over coal. From their lower environmental impact and higher efficiency to their wider availability and accessibility, pellets emerge as a cleaner, more cost-effective, and sustainable option.
By choosing pellets over coal, we can contribute to a healthier environment, reduce our carbon footprint, and move towards a more sustainable future.
FAQs on coal vs pellet
-
Are pellets better than coal?
When it comes to comfort, pellet fuel wins the run. It does not emit resinous substances when combusted, it does not make your boiler-room dirty when stored, pellet stoves and pellet are modern and almost maintenance-free.
-
Why are wood pellets better than coal?
As the main fuel of industrial boilers, wood pellet replace coal, heavy oil and natural gas, which can reduce the air pollution. In addition to, wood pellet doesn’t contain sulfur and phosphorus that will reduce corrosion and prolong service life of boilers. Power generation.
-
Which is cheaper coal or wood pellets?
Anthracite coal costs a lot less than wood pellets per unit of heat (BTU). A pound of Anthracite coal has almost twice the heat as a pound of wood pellets, therefore pellets have to be almost 1/2 the cost of Anthracite coal to be at the same cost per unit of heat.
-
Do wood pellets burn cleaner than coal?
Burning wood pellets releases as much or even more carbon dioxide per unit than burning coal. Ginther says that the U.S.’s wood pellet industry can expect even more robust growth if the Asian commercial market or European residential market embraces the combustion of wood biomass.
Originally posted 2023-11-06 07:28:52.
